Pervaporation (PV) is an effective membrane separation process for organic dehydration, recovery, and upgrading. However, it is crucial to improve membrane materials beyond the current permeability-selectivity trade-off. In this research, we introduce machine learning (ML) models to identify high-potential polymers, greatly improving the efficiency and reducing cost compared to conventional trial-and-error approach. We utilized the largest PV data set to date and incorporated polymer fingerprints and features, including membrane structure, operating conditions, and solute properties. Dimensionality reduction, missing data treatment, seed randomness, and data leakage management were employed to ensure model robustness. The optimized LightGBM models achieved RMSE of 0.447 and 0.360 for separation factor and total flux, respectively (logarithmic scale). Screening approximately 1 million hypothetical polymers with ML models resulted in identifying polymers with a predicted permeation separation index >30 and synthetic accessibility score <3.7 for acetic acid extraction. This study demonstrates the promise of ML to accelerate tailored membrane designs.
Workflow of ML-model-assisted polymer screening. (A) Prediction model development using the MFF: Generation of MFF from the simplified molecular input line system (SMILE) expression of polymers’ repeating units. For model development, different model processing methods are involved, including missing data management (MDM), DLM, and PCA. (B) The developed ML models are then implemented for high-throughput screening of hypothetical polymers in the PI1M data set (N = 995,799) with promising acetic acid extraction performance; the evaluation metrics include similarity score, PSI, and SA score.
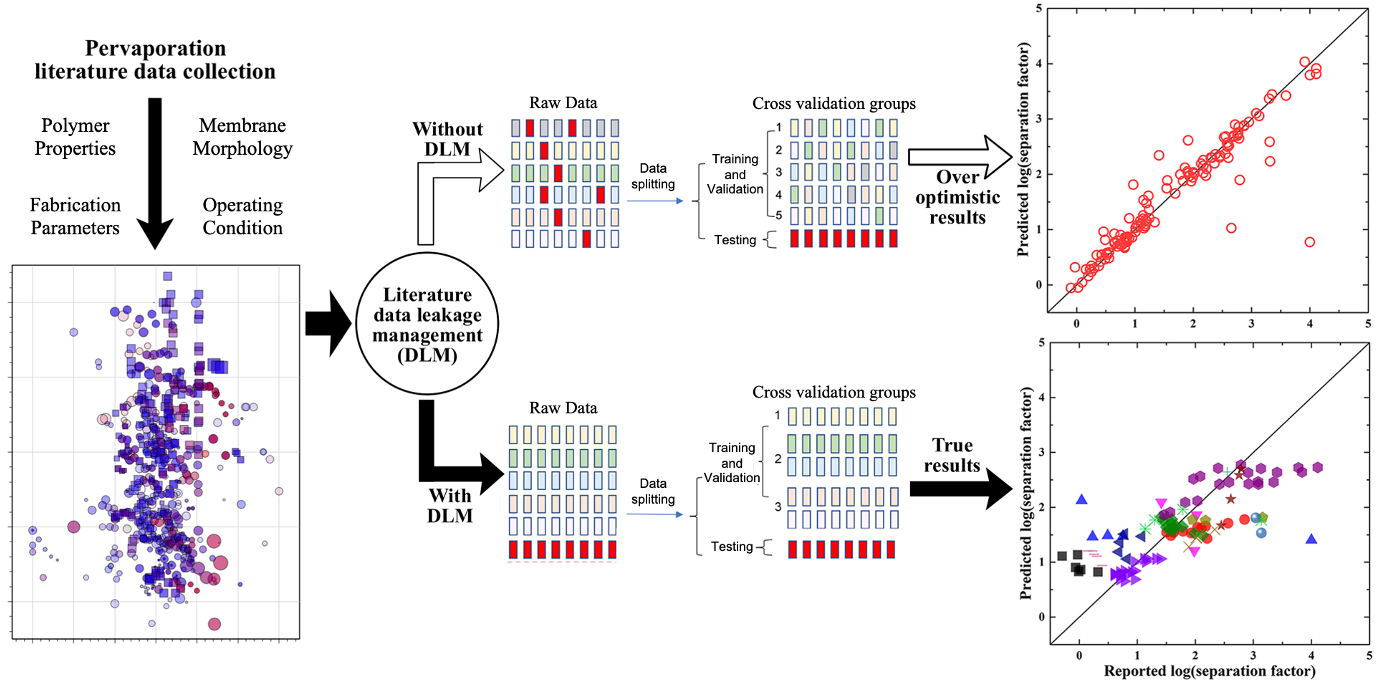
To avoid data leakage due to literature data associated with similar experimental information, we developed the first DLM-based data segmentation algorithm to treat multiple data points from the same publication as a bundle in the data splitting, so they were not split into different datasets. DLM ensures that the model makes truthful predictions for unfamiliar situations, such as new membrane materials and operating conditions.
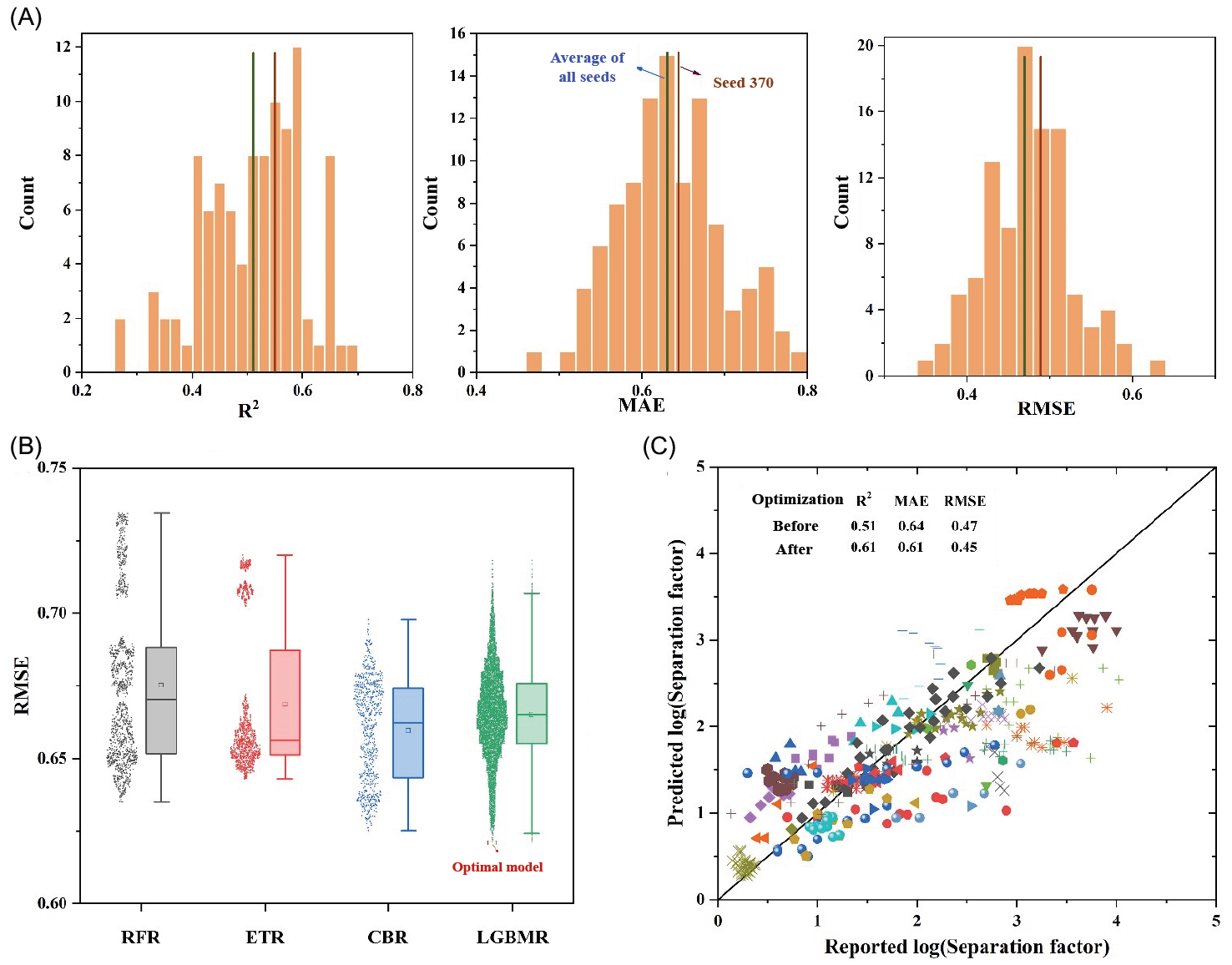
Model development and prediction results for the separation factor. (A) Primary seeds assessment using R2, MAE, and RMSE based on the testing data set using CBR. (B) Box plots showing performance (RMSE) comparison between RFR, ETR, CBR, and LGBMR using DLMbased data segmentation and a predefined CV approach based on the training data set (seed 370). (C) Comparison between reported and predicted separation factor (logarithmic) data based on the testing data set using the optimal LGBMR model; note that data from the same (anonymous) study are shown in the same mark. Prediction performance using the testing data set before and after optimization is also displayed.
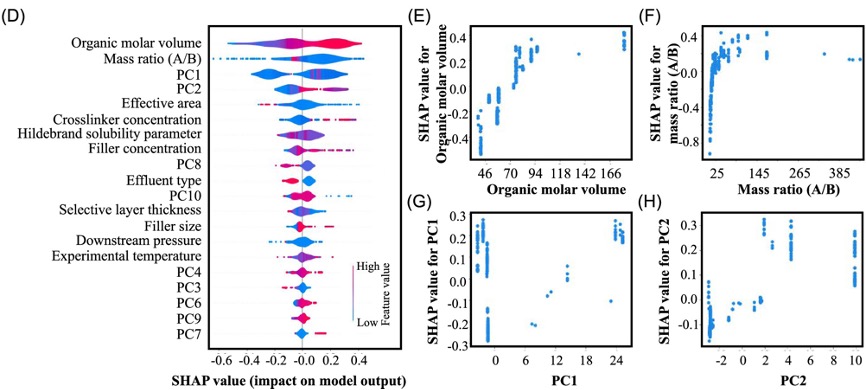
(D–H) Model interpretation by analyzing the contribution of features using SHAP for separation factor prediction. SHAP summary plot of (D) features’ contribution, (E) organics’ molar volume, (F) mass ratio, (G) PC1, and (H) PC2.
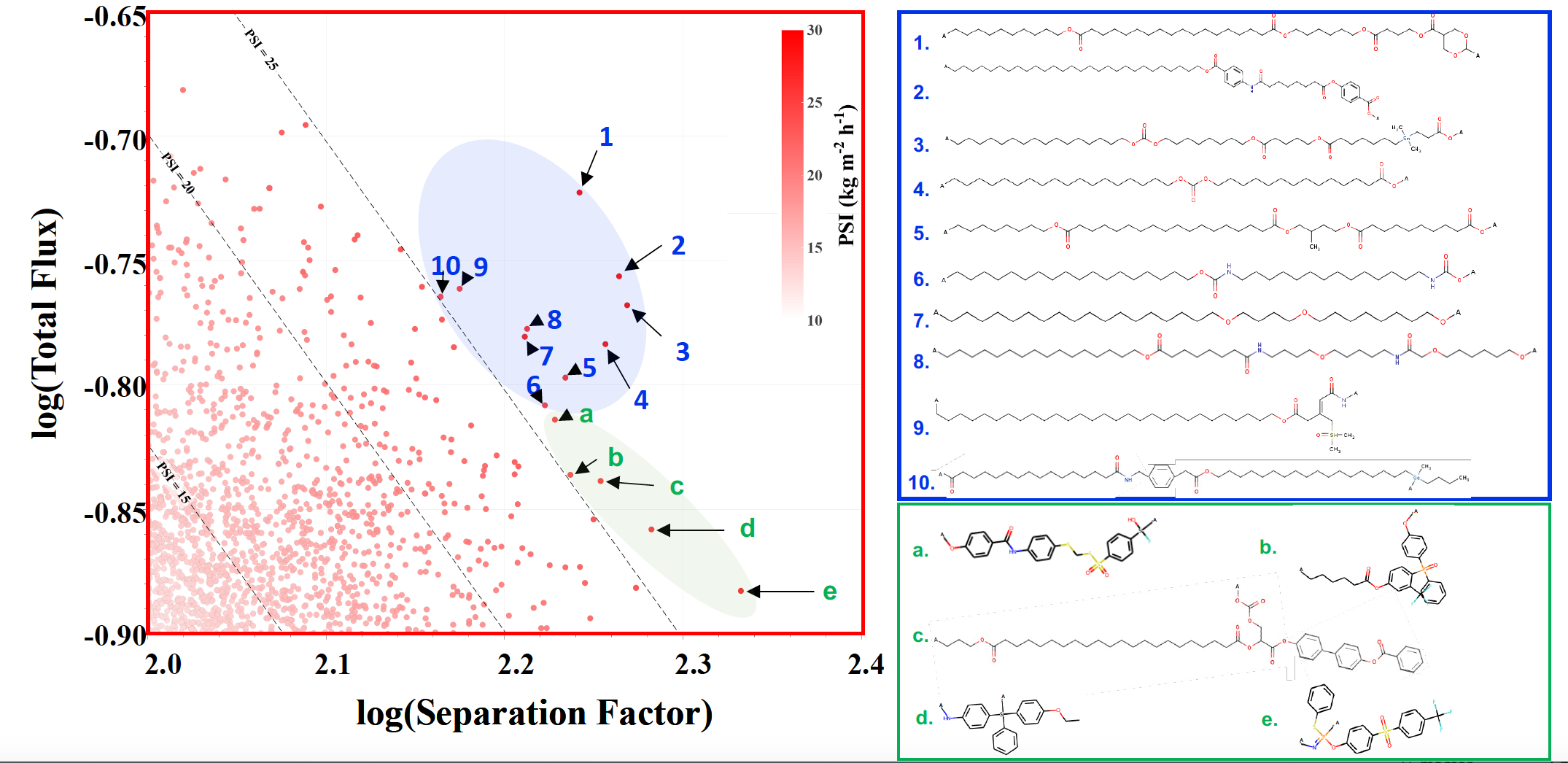
Screening of polymers from PI1M data set. (A) Summary of predicted PV performance of polymers in PI1M data set. The light-yellow slice means the critical value 5, as the current state-of-the-art PSI for acetic acid extraction is 4.6. (B) Expanded graph indicating screened polymers with the highest predicted PSI. The dashed lines represent PSI = 15, 20, and 25. (C) Highlight polymers in (B), where “A” indicate the polymerization points.
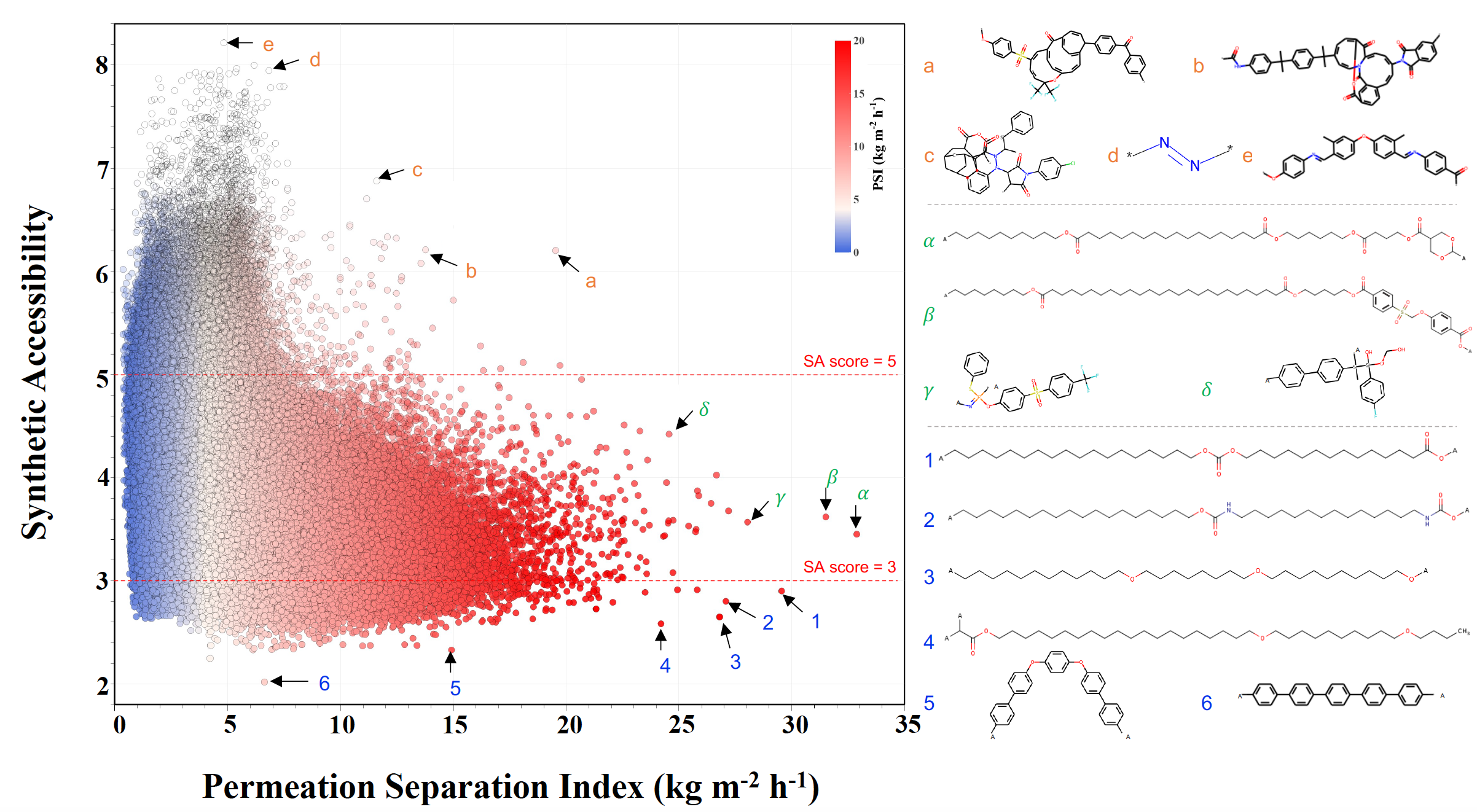
Evaluation of the synthetic accessibility and permeation separation index of correlated polymers in the PI1M data set, where “A” indicate polymerization points.
Please read more in our work (Yang et al., 2024) and (Yang et al., 2023).